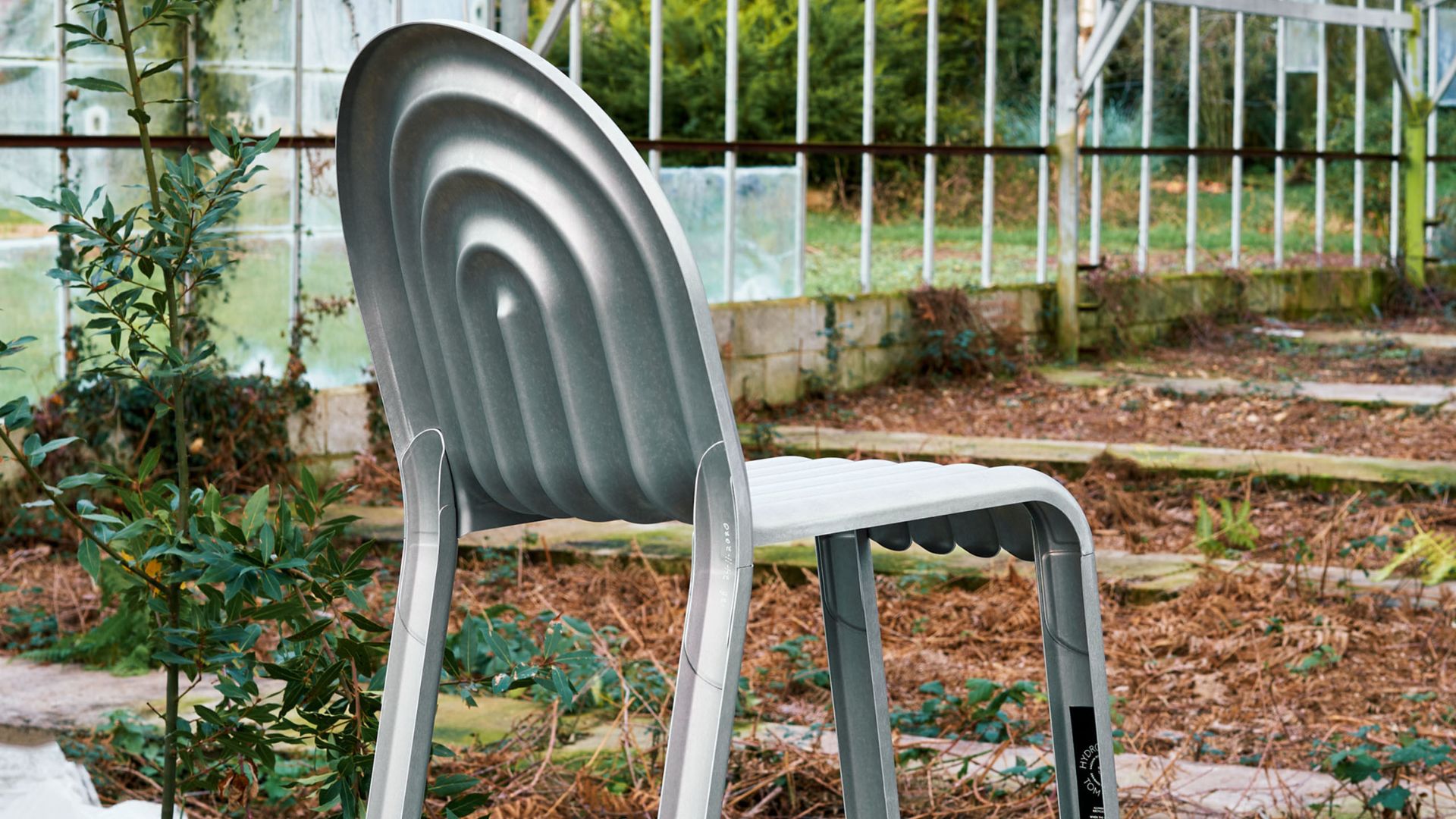
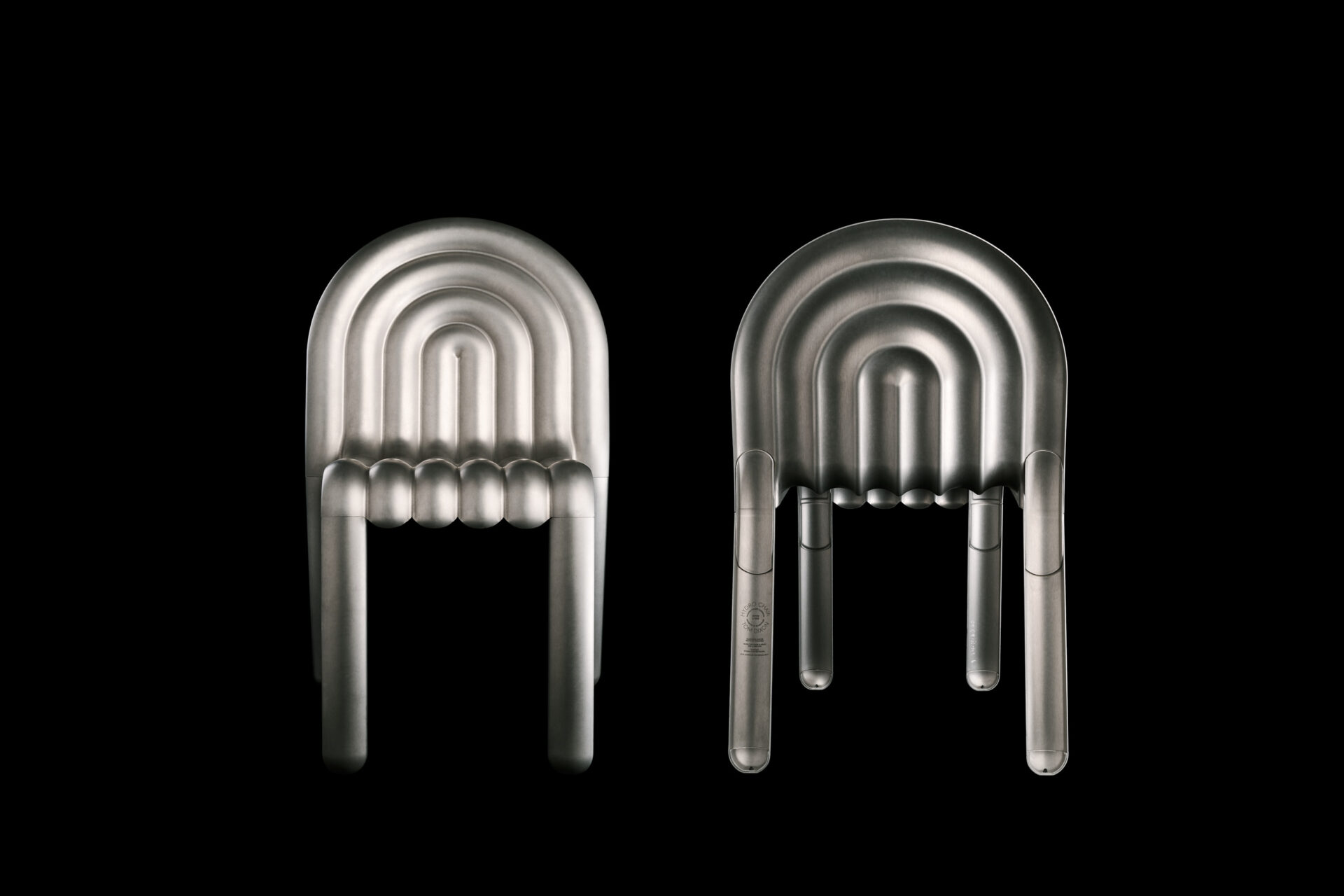
Shaping a chair from a super thin aluminum sheet

With sustainability in mind, using the right materials and the most suitable way to work with them has become a key skill for designers: the challenge being figuring out which ones are sustainable at a manufacturing level, avoiding raw material waste during production and keeping away from design solutions that make it difficult to break a product down into its components.
Is aluminum a sustainable material?
In terms of environmental impact, aluminum seems a reasonable choice: it’s light, durable and fully recyclable.
In fact, as long as it is treated correctly, it’s one of the few materials that can be recycled over and over again without losing its properties: the apparently ideal choice for a circular economy.

Yet, not all aluminum is the same.
Aluminum production is extremely energy-intensive: so its degree of eco-mindness is strictly connected to the type of energy that was used to make it.
Aluminum produced with coal power, for instance, can have factor ten in C02 emissions compared with the same material but produced with hydro power or through the use of recycled matter. Doubtless, another factor weighing on the energy balance is the amount of raw material used.
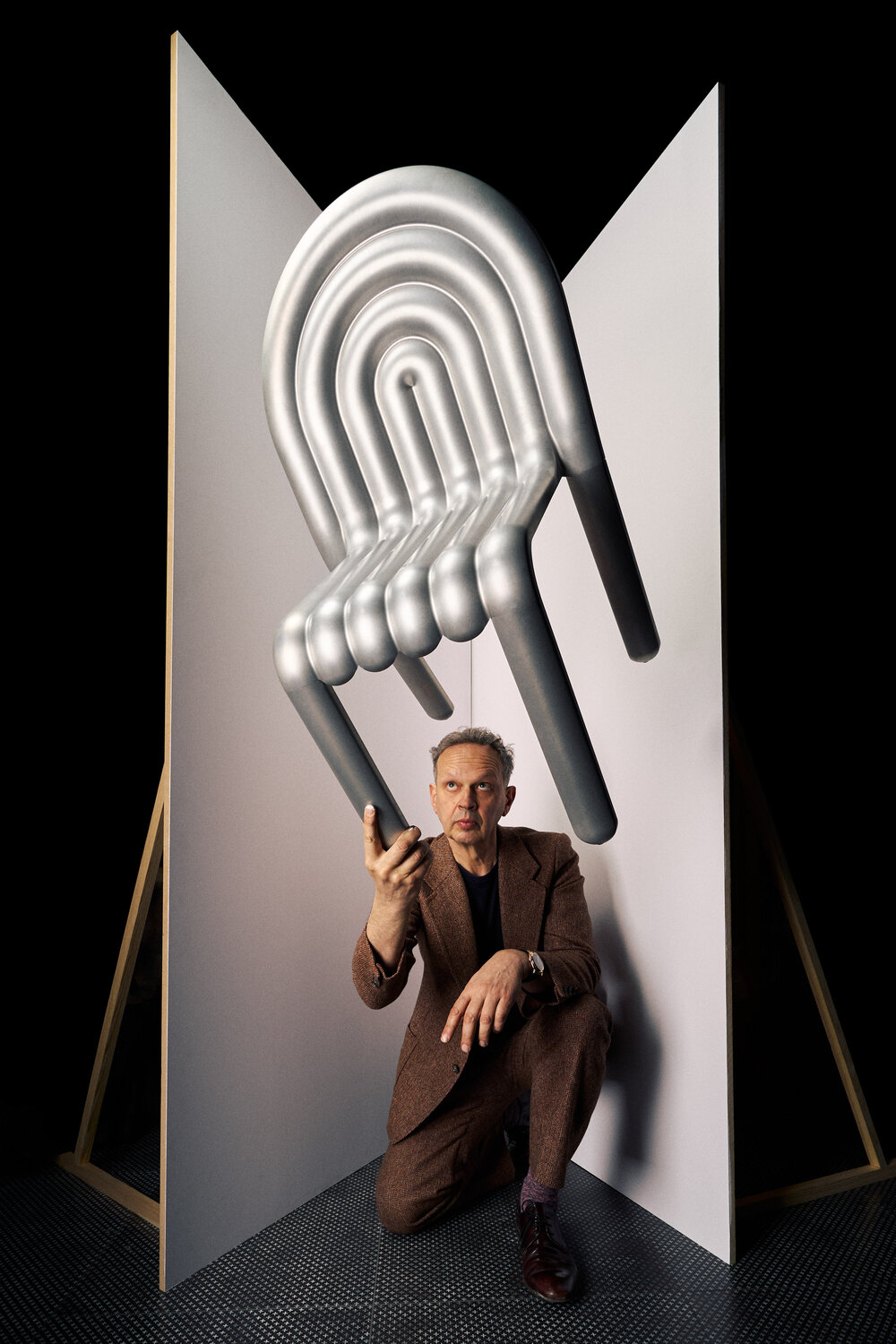
Wishing to experiment with sustainable aluminum in furniture (and being able to leverage costs and investments through his own limited edition pieces sales channel) UK designer and entrepreneur Tom Dixon contacted Norwegian aluminum giant Hydro (committed to using renewable energy in production).
His idea was to make a superlight chair, using as little material as possible while losing no stability.
The Hydro’s technical experts and the team from Tom Dixon Studio first met in late 2018, just months after the Norwegian giant’s release of new aluminum alloys specifically developed for the superplastic forming of aluminum sheets.

What is superplastic forming (and why using aluminum was a challenge)
Superplastic forming is a process that the automotive industry relies on for the production of deep drawn, thin-walled aluminum sheet components for its mass-market vehicles.
This has however remained a niche process over the last two decades is because it has traditionally shown slow cycle times in the range of half an hour per part produced, due to the lower formability of aluminum in comparison to steel.

Since the automotive industry is accustomed to stamping processes that are able to produce components in seconds, this has been a hindrance to the expanded use of the technology when it comes to aluminum.
To increase production speed and make the superplastic moulding process more attractive to the automotive industry using aluminum,
Hydro introduced new alloys which are said to achieve higher elongation properties, improved post-forming strength, and lower cycle times for the superplastic forming process.
This new aluminium alloy (from series 5000) and the high standard achieved by the superplastic forming process were crucial to the development of the chair.
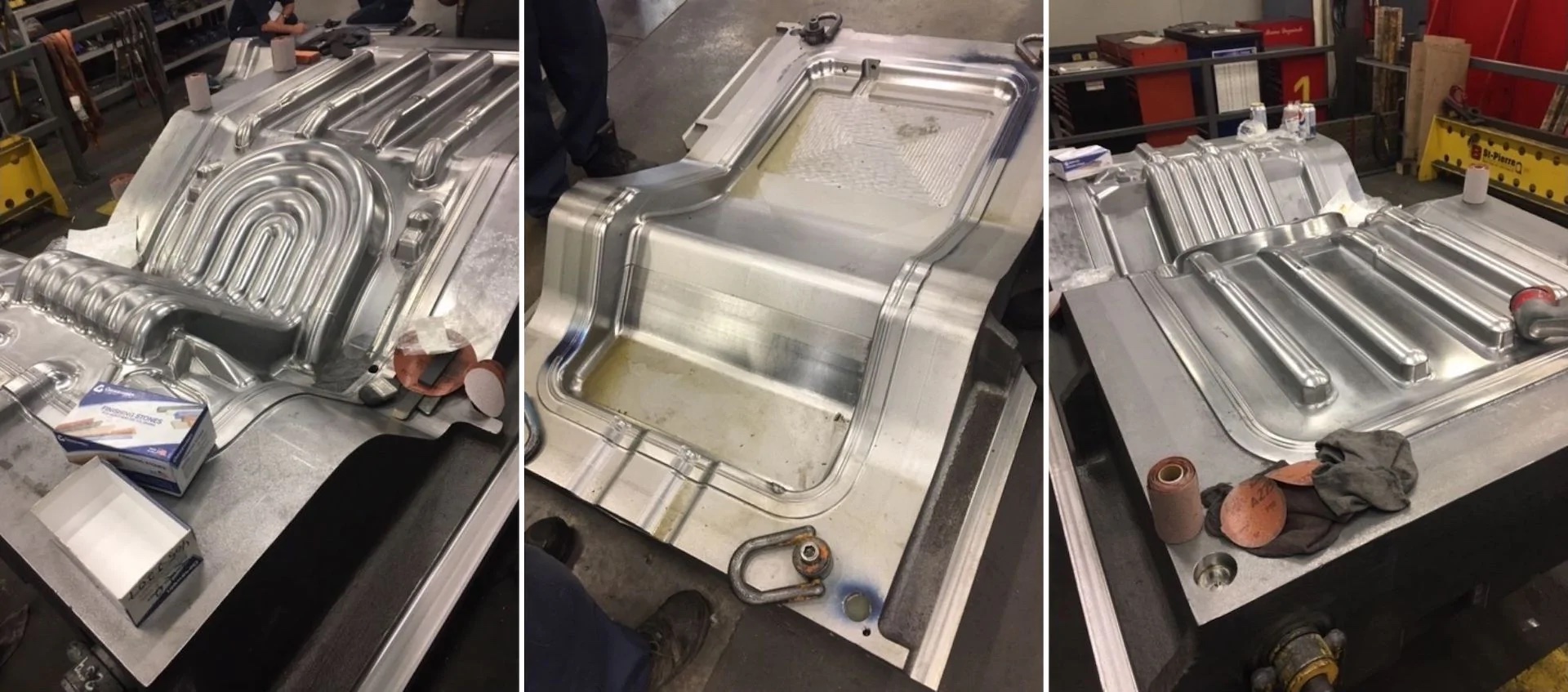
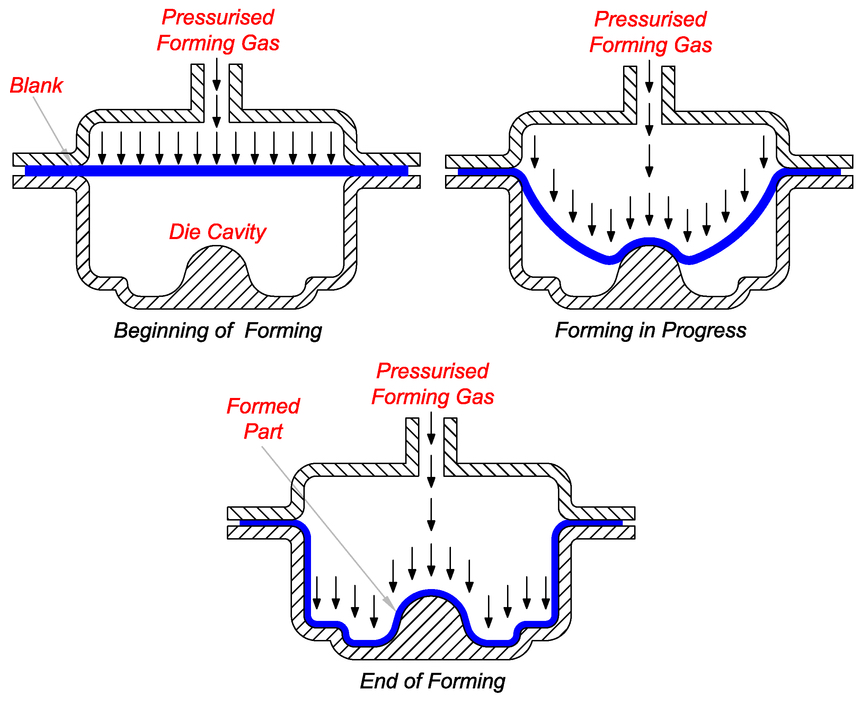
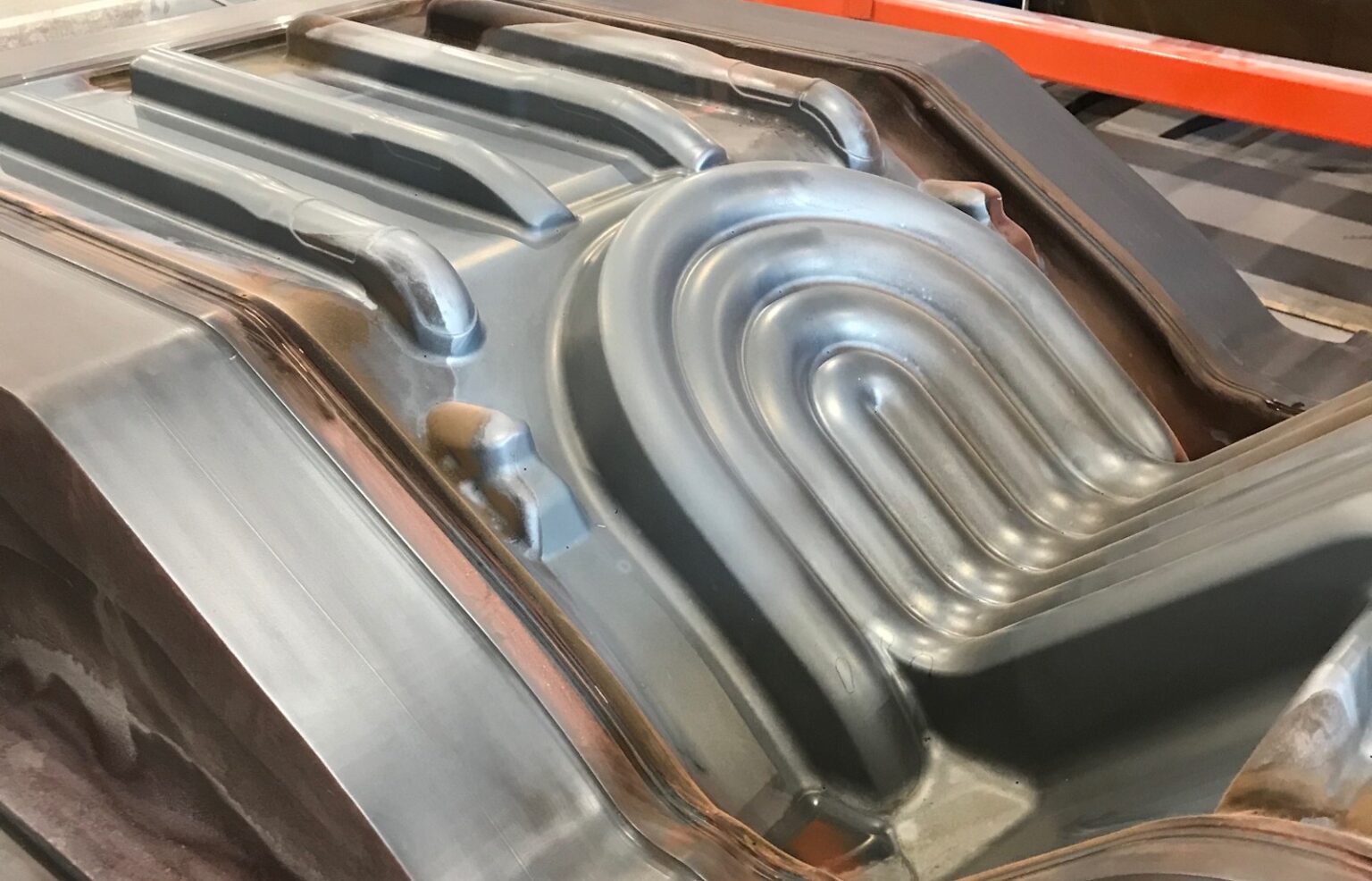
How superplastic forming was used for making the Hydro Chair
When an aluminum sheet (typically 5083 alloy) is heavily cold rolled and then heated to 450-520°C, it is able to achieve something called superplasticity.
What is superplasticity?
Superplasticity is a phenomenon, occurring in certain metals and alloys usually at high temperatures, that makes them stretch to extreme lengths without breaking.
If the material is heavily cold rolled to the point when it starts to become brittle followed by the application of heat, then the aluminum microstructure shifts to very fine grains in the range of 10 microns or less.
“The colder the forming,” explains Rösner-Kuhn, head of Products Technology & Technical Customer Service, Rolled Products, Hydro, “the more intensive the material re-crystalizes when heated, creating a new microstructure and making the material soft. The grains are able to move like wet sand, and the material forms really nicely.”
Pushing technology forward
When the material is in this heated state, the aluminum sheet is placed in a die and pressurized gas is blown onto the sheet, molding it into the formed part with no springback or residual stress.
“This process combined with the behavior of the fine grains makes it possible to create very difficult geometries, which is not possible when you do a classical stamping process,” said Rösner-Kuhn.

In a later version, the chair was also color-anodised.
Key takeaways from this story on superplastic forming of aluminum alloys
- A ballooned pattern can be obtained by blow-forming the metal (superplastic forming) at high temperatures and be laser cut to perfection: it helps minimize weight
- Connecting with manufacturers and production engineers at the earliest stages of design increases the chances of achieving innovative solutions
- Aluminum sheet in the superplastic aluminum alloy 5083T can be stretched to several times its original size without failure when heated