Step into the future – 3D-printed houses are here and in high demand
Cutting costs, saving time and eliminating waste – can 3D-printing reshape residential architecture as we know it?

Better, faster, greener. 3D-printed houses are revolutionizing the way we think about home construction, offering a sustainable, cost-effective, and highly customizable alternative to traditional building methods.
Go to:
Gallery
Open full width
Open full width
Gallery
Close full width
Close full width
With 3D printing seamlessly replacing a traditional building system and pushing the current limits of innovation – the future of homebuilding has changed. A reality synonymous with smart manufacturing, 3D printing makes up a prominent part of Industry 4.0 remolding construction as we know it.
According to Grand View Research – the global market size of 3D-printed houses was valued at USD 13.84 billion in 2021 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.8% from 2022 to 2030. Globally, 2.2 million units of 3D printers were shipped in 2021 and the shipments are expected to reach 21.5 million units by 2030.
Competing to develop the best technology, industry players have been further engaged in a space race of sorts – literally too, with even NASA brilliantly utilizing and reaping the benefits of 3D printing.

What are the benefits of 3D printing?
With the construction industry facing times of uncertainty due to a lack of skilled workers, increased costs, global housing shortage, disaster-hit regions and the effects of climate change – refreshingly new digital and sustainable capabilities of additive manufacturing is here to help.
Since 3D printing allows for high design flexibility, it’s easy to achieve a balance between form, function and aesthetics.
Without a doubt, this process offers significant potential to increase efficiency and productivity. Not only does it offer a high degree of planning reliability from the start, lowering chances of design errors and worker injuries – but it also requires low coordination and monitoring efforts. Construction time reduces drastically with this, which also translates to fewer costs.
Its environmental benefits are additionally endless. It – minimizes material use, uses natural, organic or recycled materials, generates less waste, decreases transportation needs as well as reduces carbon footprint.
How does 3D printing work?
Simply put, three-dimensional shapes are at first designed through a computer-controlled process without the use of formwork.
Skillfully utilizing a large printing machine, concrete or other materials from soil to mortar, special polymers or recycled and other plastics is extruded layer-by-layer to then effortlessly form foundations, walls, columns, stairs as well as other building elements.
Since this system is portable, it’s perfectly suitable for off-site, prefab production and in-situ application – eliminating the need for frequent relocation and calibration.
Now that you’re all caught up – scroll to explore these eclectic but one-of-a-kind 3D-printed houses that have already been built across the globe!
1. House Zero
A project that is as fascinating as it’s beautiful, construction technology company ICON and architecture studio Lake Flato present a 186-square-meter 3D-printed, modern home in Austin – House Zero.
Featuring three bedrooms with two and a half baths, along with a one bed and bath accessory dwelling unit – it stands out with its undulating forms and unique ribbed texture harmoniously blended together with a mid-century modern expression.
“House Zero is ground zero for the emergence of entirely new design languages and architectural vernaculars that will use robotic construction to deliver the things we need most from our housing – comfort, beauty, dignity, sustainability, attainability and hope” says Jason Ballard, ICON Co-Founder and CEO.
Created for net-zero energy, this climate-responsive space is built utilizing ICON’s Vulcan construction system that uses 3D printing – a technology that dispenses layers of material mechanically based on a computer program, to lay the walls of this home.
Reinforced by steel, the walls are printed within 10 days with a proprietary material ICON refers to as Lavacrete – a cement-like substance that is air-tight while additionally providing increased insulation.
While the exterior walls are composed of the soft lines of the Lavacrete – its interiors, ceiling as well as rafters are made of wood making the aura feel soothingly warm.
Timeless, rooted-to-the-earth and truly a demonstration of what living could be like – it draws attention to the natural world through its sustainable biophilic design principles.
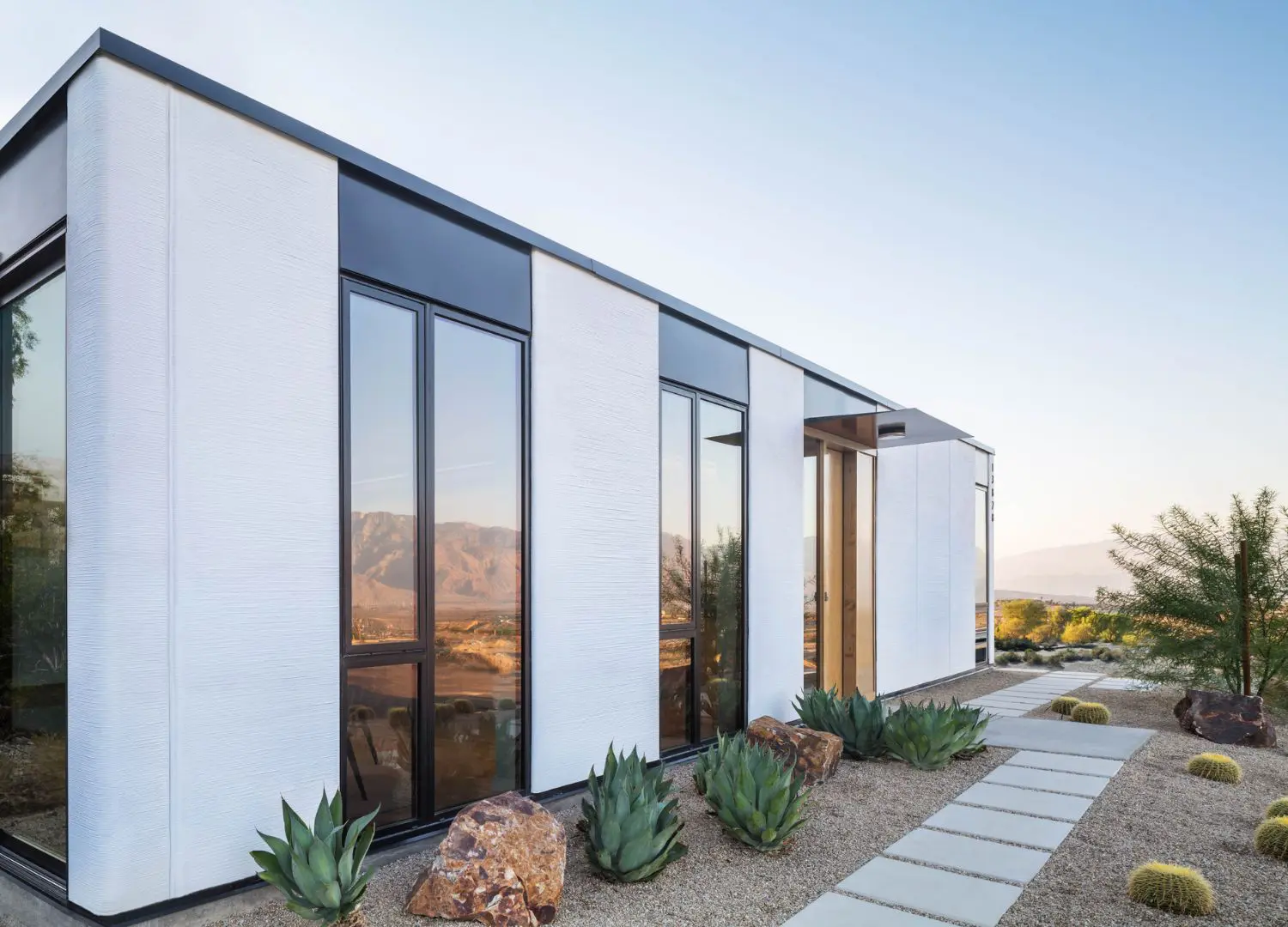
2. Mighty Buildings
Mighty Buildings completes this 159-square meter 3D-printed net-zero home in southern California as part of a 40-unit community in Desert Hot Springs that explores environmental and economic development strategies.
Ehrlich Yanai Rhee Chaney Architects (EYRC) created this alluring two-bedroom and two-bath house, known as the Quatro, which the team says will produce as much energy as it consumes using Mighty Buildings’ flexible, panelized kit of parts.
“We are excited to be the first company in the world to complete what we believe to be the sustainable housing standard of the future” says Slava Solonitsyn, CEO Mighty Buildings. “As a result, housing developers will no longer have to choose between profitability, quality, design and protecting the planet!”
The exterior composite stone wall panels have been 3D-printed in a factory in Oakland and the proprietary material – known as Light Stone – is a concrete alternative with four times more tensile and flexural strength, 30 percent less weight and less carbon dioxide, according to Mighty Buildings.
With a minimalistic material palette, it comprises white oak casework and flooring, stainless steel fixtures, glazed white tile and quartz countertops.
Along with accommodating solar technology, its robotic coating application increases resistance to hurricane winds, high water, fire, mold, insects as well as extreme temperatures.
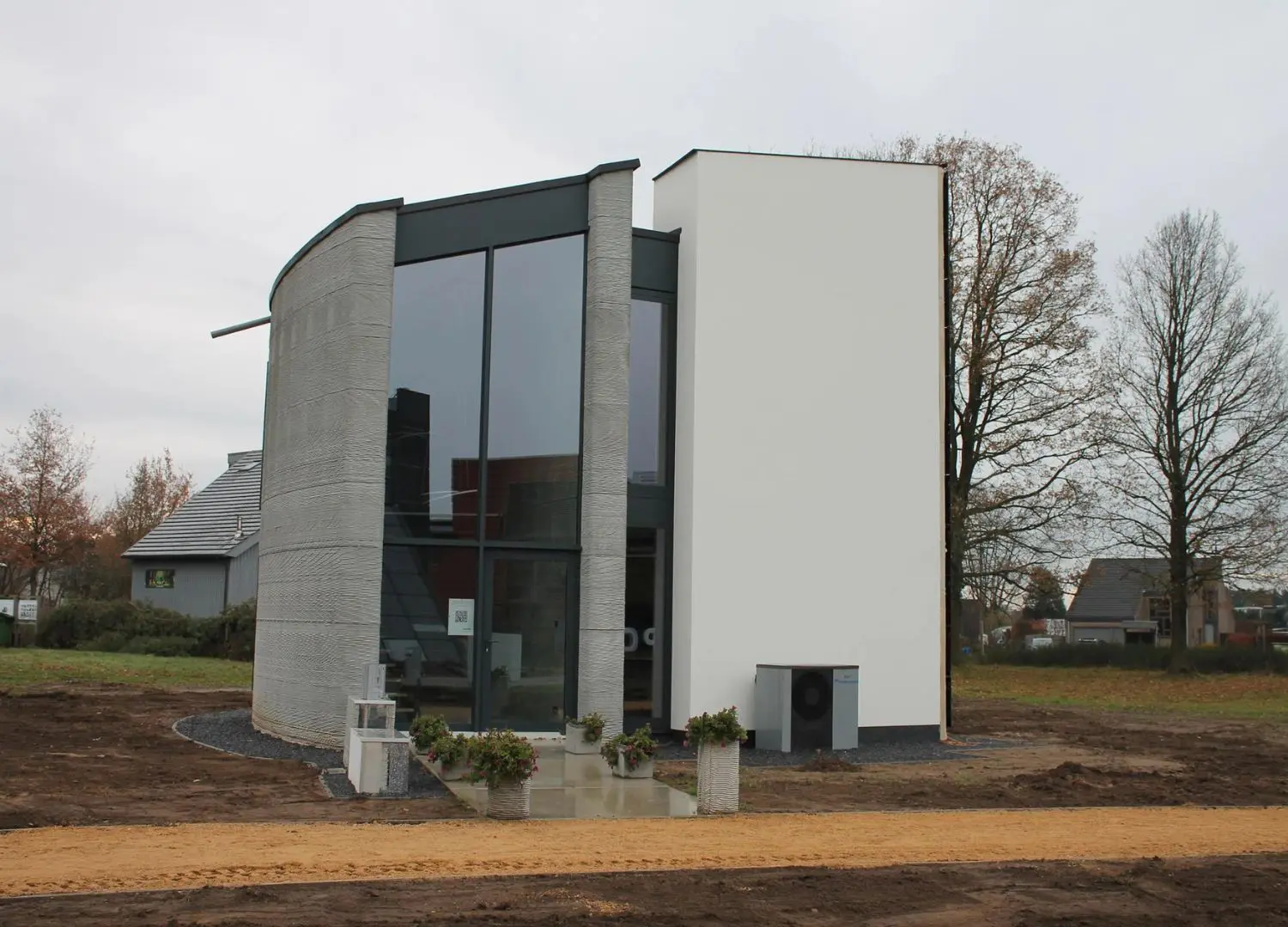
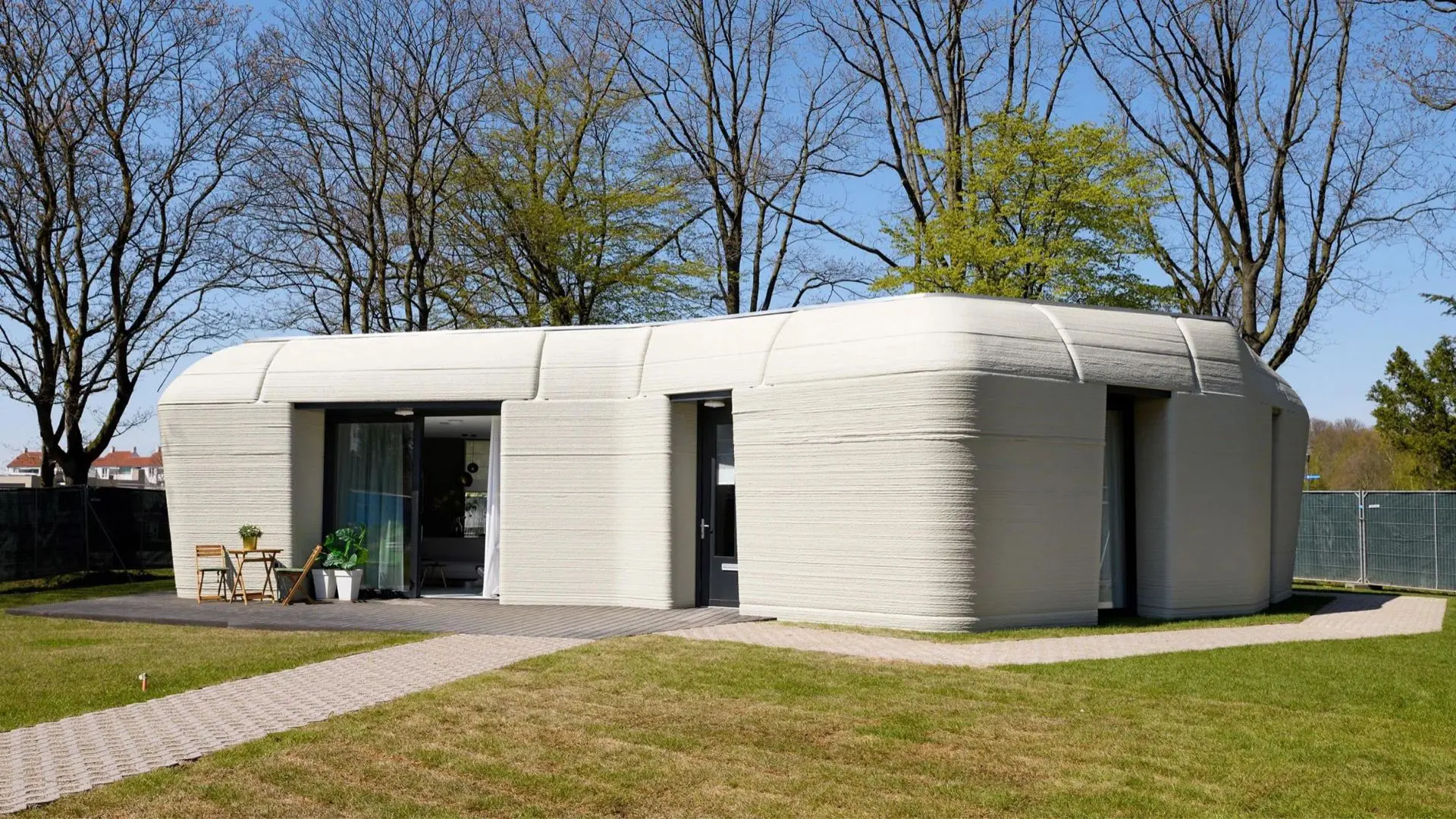
3. Project Milestone
Nestled in a suburb of Eindhoven, this 94-square-meter boulder-shaped concrete single-storey house is built as part of a five-home 3D-printing scheme named Project Milestone and designed by Dutch architects Houben and Van Mierlo.
This project marks Europe’s first legally habitable property where residential real estate investor Vesteda is the owner, renting it out to private tenants.
Embodying an organic geometry – this space includes an open-plan kitchen-diner and living area that occupies over half of the floor plan, while a large double bedroom and bathroom are contained within the remainder of the home.
Its curved, sloped exterior walls have been constructed through printing layers of stacked concrete to form 24 individual components.
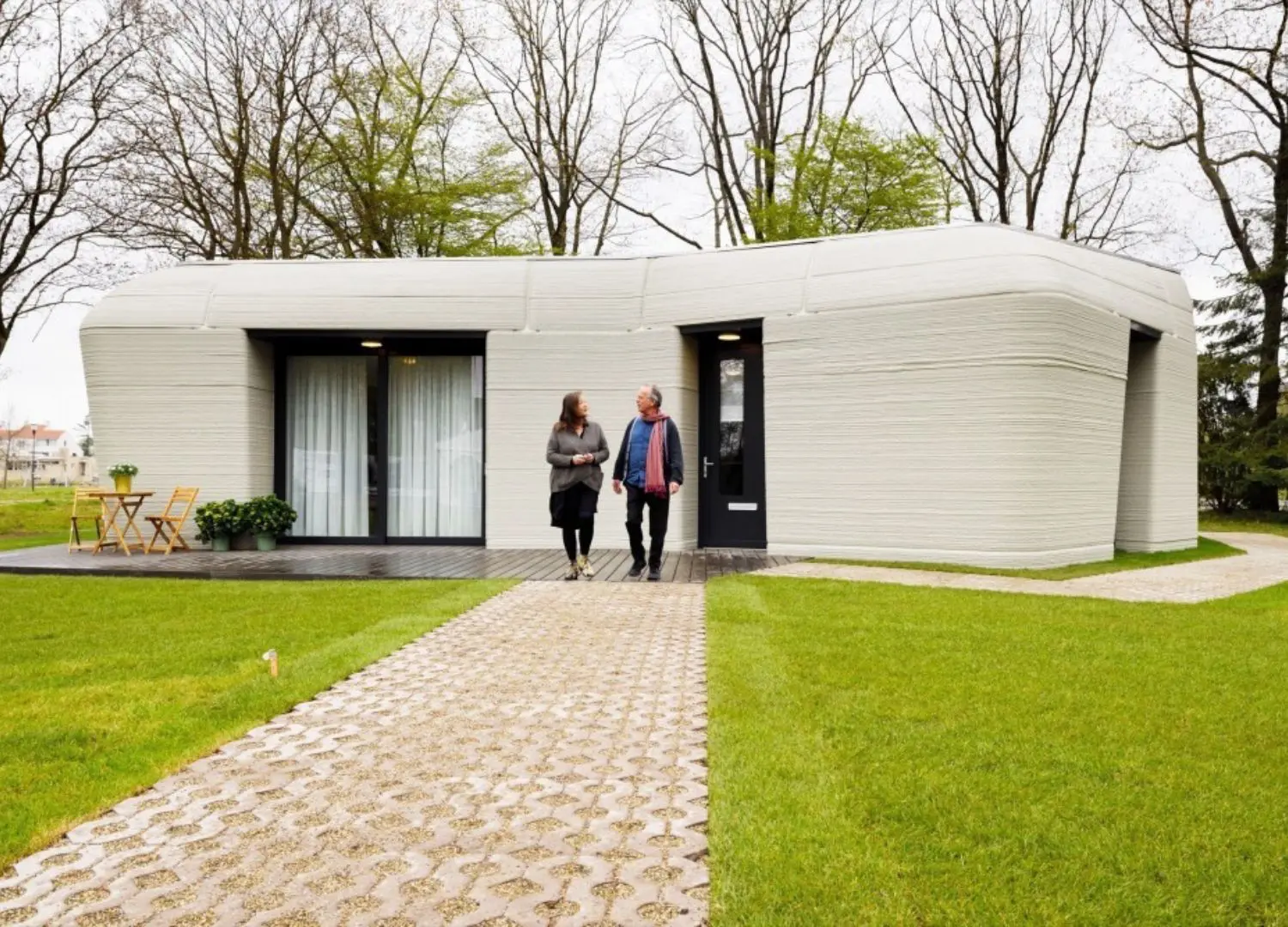

“With the printing insulated and self-supporting wall elements curved in three planes, we’ve taken important steps in this project in the further development of 3D concrete printing in construction” says Weber Benelux, CEO Bas Huysmans.
Inside, the home’s stacked concrete walls are left exposed to reveal its layered texture while the floor-to-ceiling windows interrupt the concrete layers and are recessed within its thick walls.
4. House 1.0
Built in collaboration with modular 3D construction printer company COBOD and Saga Space Architects, 3D-printing startup 3DCP Group unveils House 1.0 – the first 37-square meter 3D printed concrete home in Europe based in Holstebro.
Encompassing triangular volumes arranged circularly and connected by an open middle core, this small house is created to be as affordable as possible while comprising all necessary amenities featuring – a living room, an open-plan kitchen, a bedroom and bathroom.
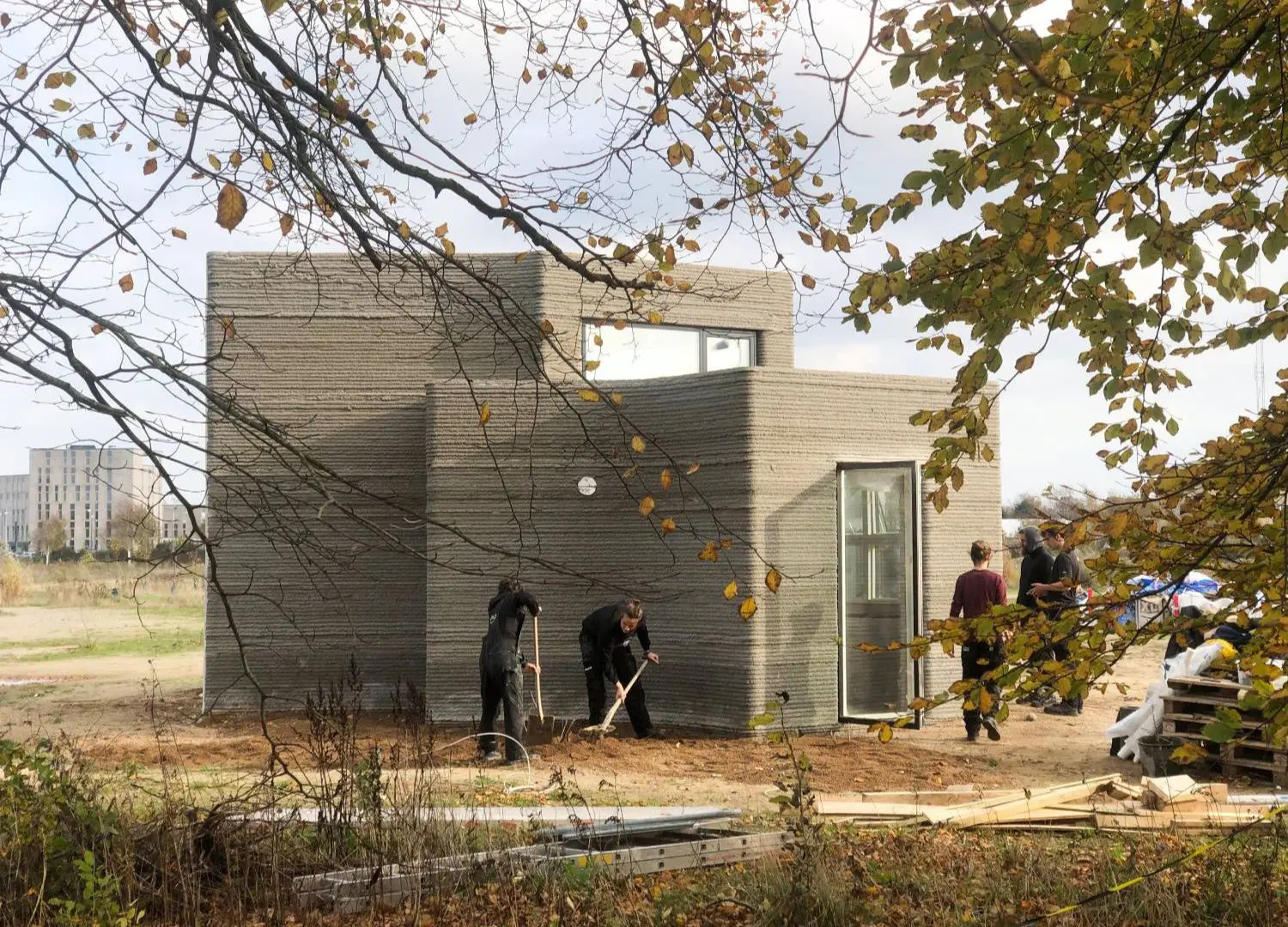

The entire building, including its roofs and foundations, is made of low-cost real concrete using a large construction 3D printer by COBOD.
Meanwhile, its interior is characterized by warm wood, responding to Nordic building traditions.
“We can offer this at a price that is far below what it would cost using conventional construction methods!” says 3DCP.
5. Kamp C
Printed in one piece with Europe’s biggest 3D printer and the world’s first – this 90-square meter two-story home by Kamp C is sited on grounds in Westerlo.
Printed as part of the European C3PO project with support from the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) – the idea behind this house was to use the achievement to encourage the construction industry to implement 3D concrete printing in their techniques.
Stronger than a home built with quick building blocks – “the compressive strength of the material is three times higher than the classic rapid building block” says Marijke Aerts, Project Manager Kamp C.
Its printing technique makes the concrete formwork superfluous, saving an estimated sixty percent of the material, time and money.
In addition to the fibers contained in the concrete, only minimal shrinkage reinforcement was utilized. If one adds up all the printing days – this entire space will be printed in less than three weeks!
6. Tecla
Bologna-based architecture studio Mario Cucinella Architects and 3D-printing specialists WASP collaborated to create a 60-square meter low-carbon housing prototype named Tecla – a combination of the words technology and clay.
Developed as part of an eco-sustainability research study, this structure is 4.2 meters in height and comprises a living space, kitchen, and sleeping area with an organic aesthetic and is fitted with services as well as a circular skylight on its roof.
Designed utilizing clay sourced locally from a nearby riverbed and printed in Massa Lombarda – this home is formed of two connected dome-shaped volumes with a ribbed outer wall that is made up of 350 stacked layers of 3D-printed clay.
Providing structural stability and acting as a thermal barrier, the prototype was constructed using a modular 3D printer that utilizes two synchronized arms, each with a 50-square meter printing area that can print modules simultaneously.
By using this technology, housing modules can be built within 200 hours while consuming an average of six kilowatts of energy and reducing typical construction waste.
Weaving together ancient building techniques with modern technology to form recyclable, low-carbon, climate-adaptable housing – “we like to think that Tecla is the beginning of a new story!” says Mario Cucinella Architects.
7. BioHome3D
The University of Maine Advanced Structures and Composites Center (ASCC) unveils BioHome3D – the first 56-square meter 3D-printed house made entirely with bio-based materials on the world’s largest polymer 3D printer.
Comprising 3D-printed floors, walls and roofs of wood fibers and bio-resins, the home is fully recyclable and highly insulated with 100% wood insulation and customizable R-values.
Construction waste was nearly eliminated due to the precision of the printing process.
Given Maine’s chilly and blustery climate, the team plans to use sensors to monitor the structure’s hardiness, as well as recycle it five times, which means that the materials will be put through a grinder, remade into a letter form and utilized again in 3D printing.
“The process is repeated five times to evaluate five recycling opportunities that may cover 500 to 1000 years of reuse!” they say.
8. East 17th Street Residences
Meticulously designed by Logan Architecture, developed by 3Strands and built from 3D-printed concrete by construction technology company ICON – East 17th Street Residences has been completed in the heart of the East Austin community.
Featuring stunning two two-bedroom homes and two four-bedroom homes, that took five to seven days to print each – the ground-floor walls were built using ICON’s Vulcan construction system, which utilizes a robotic armature to layer the Portland-cement-based material Lavacrete into striated surfaces.
This process created a stronger and longer-lasting building material compared to traditional techniques, making the houses tougher in the face of extreme weather.
The interiors were designed by Austin-based Claire Zinnecker – “who chose a simplified color palette of green, white and terracotta as well as fixtures that play off the natural materials” says ICON.
The open-plan spaces further have a neutral muted palette with wood cabinetry, woven rugs and touches of greenery.
9. Wolf Ranch
In what is set to become the “largest-scale development of 3D-printed homes globally,” Danish architecture studio BIG and American 3D-printing firm ICON have successfully completed a full-sized model home.
Situated in the Wolf Ranch neighborhood of Georgetown, Texas, near Austin, this pioneering house represents a collaboration between Bjarke Ingels Group (BIG) and ICON. As part of an ambitious project, local construction firm Lennar is currently working on the construction of 100 houses, with this particular home serving as an exemplary model for prospective buyers.
The community of 3D-printed homes seamlessly combines the timeless charm of contemporary Texas ranch style with elevated architectural elements and energy-efficient designs. These innovative homes showcase the advantages of resiliency and sustainability, achieved through the cutting-edge possibilities of additive construction.
Utilizing ICON‘s Vulcan robotic construction systems, sophisticated software, and advanced materials, these homes are swiftly and efficiently delivered at scale. The construction process minimizes waste and provides unparalleled design freedom by 3D-printing the entire wall system, both interior and exterior walls.
What type of materials can be used?
3D-printed houses offer a wide range of material options that can be used to construct these innovative structures. One commonly used material is concrete, which is sturdy, durable, and readily available.
Concrete mixtures specifically formulated for 3D printing enable the printers to layer the material effectively. Another material gaining popularity is bioplastics, derived from renewable sources such as cornstarch or algae.
These materials are eco-friendly and can be easily melted and extruded by the printers. Additionally, composite materials, such as a combination of fibers and resins, are being explored for their high strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility in design.
It’s worth noting that ongoing research and experimentation continue to expand the range of materials that can be used in 3D-printed houses, opening up possibilities for sustainable and cost-effective construction.
3D-printed houses: what’s next?
To truly imagine a future where 3D printing becomes the norm for mass housing – there are still many challenges to overcome in order to replace traditional methods. From adapting to countries’ strict construction requirements, addressing high-density areas, responding to varying weather conditions, improving the circularity of materials, reducing its carbon footprint and making the technology even more affordable.
It all starts, nonetheless, by continuing to invest, explore and innovate. These successfully 3D-printed houses certainly point the industry in the right direction and even though there’s still a lot of potentials to be explored in other markets – it’s clear that 3D construction printing is here to stay.