EcoLattice, an advanced material reinventing foam technology
By integrating advanced fabrication techniques with circular economy principles, this material showcases how to significantly reduce waste while maintaining functional performances.

The global challenge of managing foam waste has prompted a re-evaluation of traditional manufacturing practices. EcoLattice is a material developed from recycled thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), specifically formulated to create 3D-printed lattice-foams.
Compared to traditional foamed and cushioning materials, that are generally expanded during production via large scale thermal and pressure driven transformations, this approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also somewhat redefines the potential of such structured materials in modern design and engineering.
Gallery
Open full width
Open full width
Key oroperties of EcoLattice
The material’s lightweight nature makes it ideal for applications requiring minimal structural load, while its fire-resistant properties enhance safety in diverse environments. As the lattice structure is totally customizable, resulting foams can showcase tailored density areas and mechanical properties to meet specific use cases. Additionally, the almost zero-waste production process ensures that no material is discarded during manufacturing. The intrinsic resistance of the material to microbial growth further extend the utility of so-created foam structures in healthcare and hygiene-sensitive settings.

Diverse applications across industries
The versatility of these designed foam structures spans multiple sectors. In wellness, they are used for ergonomic support systems and adaptive seating. For interiors, the material’s aesthetic flexibility and durability make it suitable for furniture, wall panels, as well as acoustic solutions. In the automotive industry, optimized lattice foams provide lightweight components for vehicle interiors, contributing to fuel efficiency. Looking beyond these sectors, the material’s adaptability extends its application to packaging or even sports equipment.
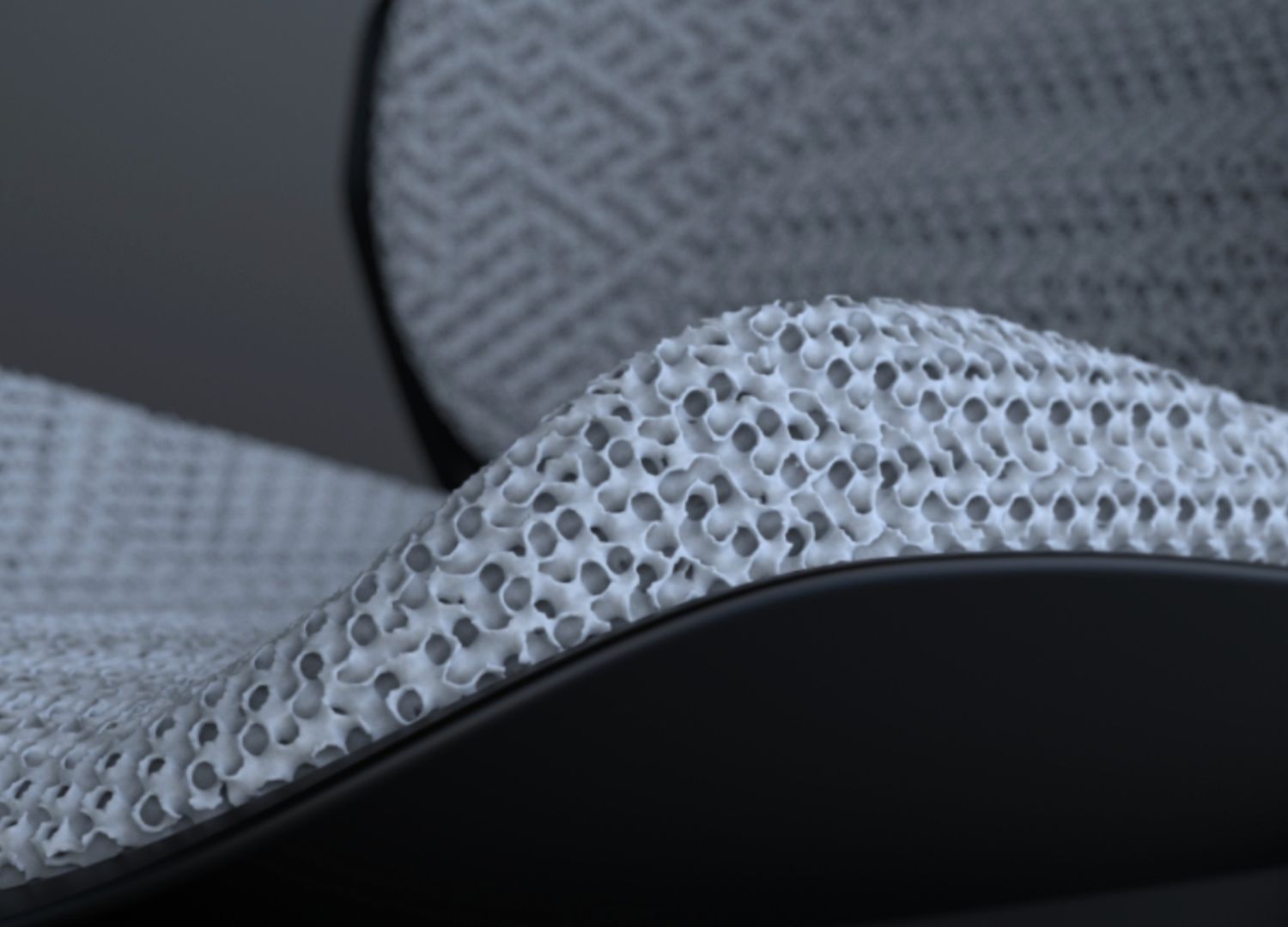
Production formats and technical range
The material is available in shore hardness values between 20A and 80A, catering to varying load-bearing and comfort requirements and is supplied in a range of formats, from standardized cushion profiles to custom-engineered components. Production utilizes FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling) technology, ensuring precision and scalability. The supply chain emphasizes transparency, with raw materials sourced from post-consumer waste, factory trims, and recycled elastomers.

Toward a circular future for foam-based design
EcoLattice’s lattice foams exemplify how material science can drive the progress between environmental responsibility and industrial performance, by prioritizing recyclability, reducing waste, and enabling on-demand customization, Its use of recycled thermoplastic polyurethane offers benefits such as the use of secondary raw materials, lower carbon emissions, and compliance with environmental standards. Although challenges like feedstock variability and recycling infrastructure exist, its adaptability and long-term advantages make it a competitive alternative to conventional foam materials

















